The impacts of global warming are likely to be "severe, pervasive and irreversible", a major report by the UN has warned.
Scientists and officials meeting in Japan say the document is the comprehensive assessment to date of the impacts of climate change on the world.
Members of the UN's climate panel say it provides overwhelming evidence of the scale of these effects.
Natural systems now bear the brunt, but a growing impact on humans is feared.
Our health, homes, food and safety are all likely to be threatened by rising temperatures, the summary says.
The report was agreed after almost a week of intense discussions here in Yokohama.
This is the second of a series from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) due out this year that outlines the causes, effects and solutions to global warming.
This latest Summary for Policymakers document highlights the fact that the amount of scientific evidence on the impacts of warming has almost doubled since the last report in 2007.
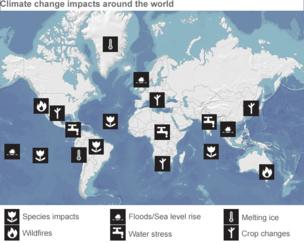
Be it the melting of glaciers or warming of permafrost, the summary highlights the fact that on all continents and across the oceans, changes in the climate have caused impacts on natural and human systems in recent decades.
In the words of the report, "increasing magnitudes of warming increase the likelihood of severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts".
"Nobody on this planet is going to be untouched by the impacts of climate change,'' IPCC chairman Rajendra Pachauri told journalists at a news conference in Yokohama.
"Before this we thought we knew this was happening, but now we have overwhelming evidence that it is happening and it is real," said Dr Saleemul Huq, a convening lead author on one of the chapters.
Michel Jarraud, secretary-general of the World Meteorological Organization, said that, previously, people could have damaged the Earth's climate out of "ignorance".
"Now, ignorance is no longer a good excuse," he said.
The report details significant short-term impacts on natural systems in the next 20 to 30 years. It details five reasons for concern that would likely increase as a result of the warming the world is already committed to.
These include threats to unique systems such as Arctic sea ice and coral reefs, where risks are said to increase to "very high" with a 2C rise in temperatures.
The summary document outlines impacts on the seas and on freshwater systems as well. The oceans will become more acidic, threatening coral and the many species that they harbour.
Animals, plants and other species will begin to move towards higher ground or towards the poles as the mercury rises.
Humans, though, are also increasingly affected as the century goes on.
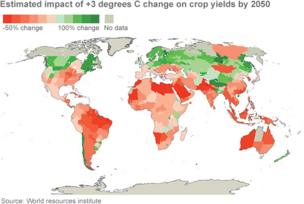
Food security is highlighted as an area of significant concern. Crop yields for maize, rice and wheat are all hit in the period up to 2050, with around a tenth of projections showing losses over 25%.
After 2050, the risk of more severe yield impacts increases, as boom-and-bust cycles affect many regions. All the while, the demand for food from a population estimated to be around nine billion will rise.
Many fish species, a critical food source for many, will also move because of warmer waters.
In some parts of the tropics and in Antarctica, potential catches could decline by more than 50%.
"This is a sobering assessment," said Prof Neil Adger from the University of Exeter, another IPCC author.
"Going into the future, the risks only increase, and these are about people, the impacts on crops, on the availability of water and particularly, the extreme events on people's lives and livelihoods."
People will be affected by flooding and heat related mortality. The report warns of new risks including the threat to those who work outside, such as farmers and construction workers. There are concerns raised over migration linked to climate change, as well as conflict and national security.
While the poorer countries are likely to suffer more in the short term, the rich won't escape.
"The rich are going to have to think about climate change, we're seeing that in the UK, with the floods we had a few months ago, and the storms we had in the US and the drought in California," said Dr Huq.
"These are multibillion dollar events that the rich are going to have to pay for, and there's a limit to what they can pay."
But it is not all bad news, as the co-chair of the working group that drew up the report points out.
"I think the really big breakthrough in this report is the new idea of thinking about managing climate change as a problem in managing risks," said Dr Chris Field.
"Climate change is really important but we have a lot of the tools for dealing effectively with it - we just need to be smart about it."
There is far greater emphasis to adapting to the impacts of climate in this new summary. The problem, as ever, is who foots the bill?
"It is not up to IPCC to define that," said Dr Jose Morengo, a Brazilian government official who attended the talks.
"It provides the scientific basis to say this is the bill, somebody has to pay, and with the scientific grounds it is relatively easier now to go to the climate negotiations in the UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) and start making deals about who will pay for adaptation."